
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a prenatal procedure that your doctor may recommend you have during pregnancy. The test checks for fetal abnormalities (birth defects) such as Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis or spina bifida. In most cases, the results are normal. Amniocentesis is performed between 16 and 20 weeks into the pregnancy.
The most common reason to have an amniocentesis performed is to determine whether a fetus has certain genetic disorders or a chromosomal abnormality, such as Down syndrome. Amniocentesis (or another procedure, called chorionic villus sampling (CVS)) can diagnose these problems in the womb.
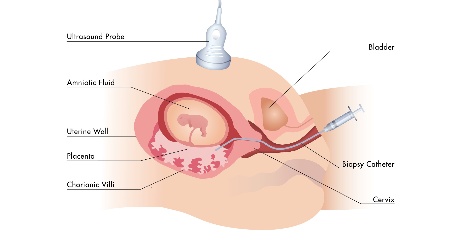
Chorionic Villi Biopsy
Chorion biopsy is an invasive diagnostic method that is mainly employed during early pregnancy (embryonic period). Normally, chorial tissue is removed trans-vaginally using a biopsy needle and examined in the direct preparation or after short-term in-vitro cultivation.
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a prenatal test that is used to detect birth defects, genetic diseases, and other problems during pregnancy. During the test, a small sample of cells (called chorionic villi) is taken from the placenta where it attaches to the wall of the uterus.
Chorionic villi are tiny parts of the placenta that are formed from the fertilized egg, so they have the same genes as the baby.
You may be offered CVS if you have certain risk factors for having a baby with a birth defect or genetic disease, so that problems can be found early in pregnancy.
Fetal Reduction
Fetal Reduction is a procedure used to reduce the number of fetuses in a multiple pregnancy, usually to two. When a pregnancy involves three or more fetuses, the risks of miscarriage, stillbirth, and structural malformation increase with each additional fetus.
Fetal reduction refers to choosing to reducea fetus in a multiple pregnancy, to decrease the health risks to the mother in carrying and giving birth to more than one or two babies, and to also decrease the risk of complications to the remaining fetuses.
It is usually done between 11 to 14weeks of pregnancy. It could be done in combination with the first trimester screening. The procedure usually does not have any adverse effect on the surviving fetus.
FAQ & Answers
>> Several hundred genetic disorders. The test is not used to look for all of them, but if thebaby is at increased risk for any particular genetic condition, CVS can usually tell whether the baby has the disease.
>> It should be noted that in case of CVS, there's a 1 to 2 percent chance of getting an unclear result. This is called a confined placental mosaicism, in which some of the cell lines cultured from the placenta contain abnormal chromosomes and some are normal. If the CVS detects a mosaicism, the patient will have to have amniocentesis and possibly other testing to determine whether the baby is affected.
>> Because it is very small during the first trimester, the reduced fetus is usually absorbed by the mother's body. This may include some vaginal bleeding.
ATTENTION!!!!
SONOSCAN SONOGRAPHY CENTRE
SHIFTING SOON TO A NEW, BIGGER & ATTRACTIVE PLACE
New Adress-
1st floor, Neel Solitaire Building, Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Chowk, Old Panvel- Navi Mumbai
9820349315 /9321349315