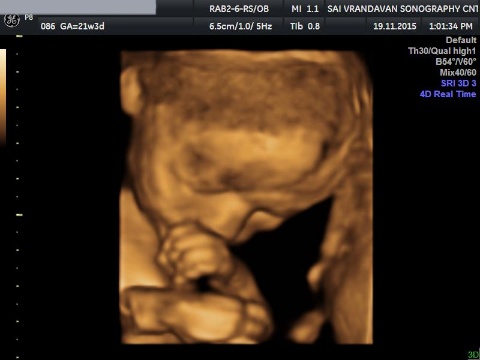
3D / 4D SCAN
3D scans are still pictures of your baby in three dimensions. 4D scans are moving 3D images of your baby, with time being the fourth dimension.
You're probably really excited by the prospect of your first scan. But some mothers find the standard 2D scans disappointing when all they see is a grey, blurry outline.
This is because the scan sees “right through” your baby, so the photos show your baby's internal organs.
Both types of scans are just as safe as a 2D scan, because the image is made up of sections of two-dimensional images converted into a picture. There's no evidence to suggest that scans aren't safe, and most mums-to-be gain reassurance from them.
These pictures show the kind of detail you can see on a 3D scan. The image on the right is of a baby at 14 weeks. With 3D and 4D scans, you see your baby's skin covering her internal organs. You may see the shape of your baby's mouth and nose, or see your baby yawn.
The special transducers and software required to do 3D and 4D scans are expensive and hence they 3D / 4D scans are costly.
3D and 4D scans may nonetheless show more detail about a known abnormality.

NT SCAN
NT Scan or Nuchal Translucency screening is nothing but an ultrasound test. Though any pregnant woman can be advised to go through this test but the main utility of this test lies in the cases involving older expecting mothers who cannot undergo other invasive medical tests such as CVS and amniocentesis due to the increased risk of miscarriage associated with them. The other set of people on whom this test is performed are with the abnormal family medical history with chromosomal disorders or any kind of problems faced with prior pregnancies. The test is used to detect the heart defects (congenital), down syndrome and other forms of chromosomal disorders that are the result of additional copies of chromosomes.
The nuchal translucency scan is done between 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy. It might need to be done alone, or it might be able to be done while you're having your dating scan. Usually the scan is done through your abdomen but occasionally the nuchal translucency can only be seen by inserting a probe into the vagina.

Viability Scan
This is a scan usually carried out trans-vaginally at 6 weeks to 10 weeks of pregnancy. The scan can determine the number of fetuses present and whether the pregnancy is progressing normally inside the uterus. It is useful for women who are experiencing pain or bleeding in the pregnancy and those who have had previous miscarriages or ectopic pregnancies. The figure shows a normal pregnancy at 7 weeks of gestation.
This is a simple procedure, in which a thin ultrasound probe with a sterile cover is gently inserted into the vagina to provide detailed pictures of the inside of the uterus. Occasionally a Fetal Viability Scan may be inconclusive, especially if the gestational age is less than 6 weeks.
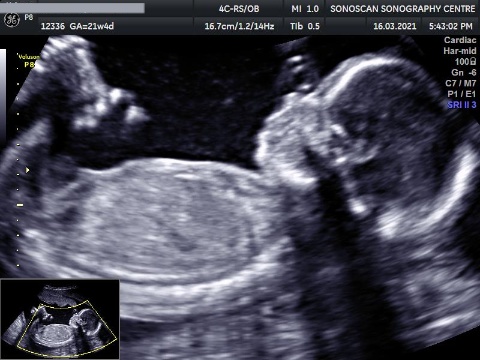
Anomaly Scan
For many couples, the 21 week detailed anatomy scan can be one of the highlights of a pregnancy. It is a wonderful opportunity to see the actual form and movements of the fetus. During the scan a specialist sonographer will measure the fetal size, examine each part of the fetal body, determine the position of the placenta and assess the amount of amniotic fluid. Special attention is paid to the brain, face, spine, heart, stomach, bowel, kidneys and limbs.
This detailed ultrasound scan, sometimes called the mid-pregnancy or anomaly scan, is usually carried out when you're between 18 and 21 weeks pregnant. The 20-week scan is offered to everybody, but you do not have to have it if you do not want to.

Color Doppler
A Doppler is a form of ultrasound scan that helps to assess your baby's health. It measures the blood flow in different parts of your baby's body, such as his umbilical cord, brain and heart. This helps to show whether he's getting all the oxygen and nutrients he needs via the placenta. A Doppler scan can be performed at the same time as a normal ultrasound and uses the same equipment. Most ultrasounds have a Doppler function. The person carrying out the scan (sonographer) will put some gel on your tummy and move a hand-held device (transducer) over your skin.
Doppler ultrasound uses sound waves to detect the movement of blood in vessels. It is used in pregnancy to study blood circulation in the baby, uterus and placenta. Using it in high-risk pregnancies, where there is concern about the baby's condition, shows benefits.

Fetal Echo
Fetal echocardiography is a test similar to an ultrasound. This exam allows your doctor to better see the structure and function of your unborn child’s heart. It’s typically done in the second trimester, between weeks 18 to 24. The exam uses sound waves that “echo” off of the structures of the fetus’ heart. A machine analyzes these sound waves and creates a picture, or echocardiogram, of their heart’s interior. This image provides information on how your baby’s heart has formed and whether it’s working properly.
An obstetrician will recommend a fetal echocardiogram when he or she suspects a fetus may have a congenital heart defect, or because he or she detected an abnormal heart rate in a standard obstetric ultrasound.

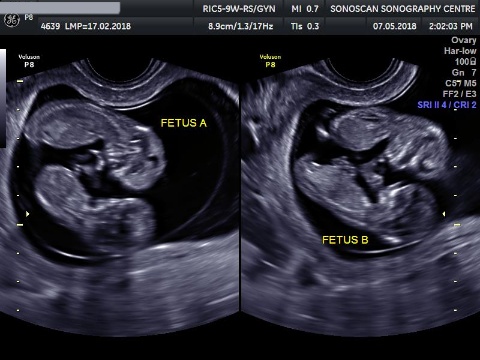
Twins
DIFFERENT TYPES OF TWINS
1. DICHORIONIC DIAMNIOTIC (DCDA) TWINS:
DCDA twins have 2 placentas and 2 separate sacs. These babies usually have different genetic material and only 10% will be identical.
2. MONOCHORIONIC DIAMNIOTIC (MCDA) TWINS:
MCDA twins have a single placenta and 2 separate sacs. These babies have identical genetic material.
3. MONOCHORIONIC MONOAMNIOTIC TWINS ( MOMO ) :
MOMA twins have a single placenta and both babies are moving around within the same sac. They also have the same genetic material.
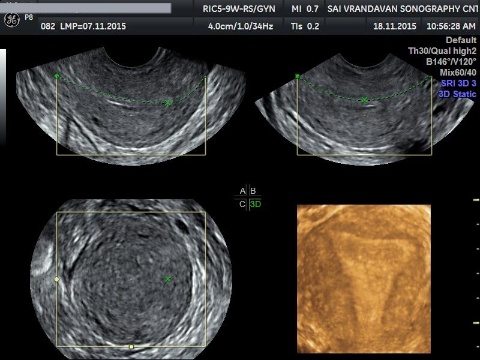
Pelvis Scan
A Transvaginal ultrasound scan may be needed to improve the detail of the pictures. If you are having Transvaginal scan the procedure will be explained to you. Following this, Your verbal consent will obtained to doctor this part of the procedure. A second lady staff member will also be in the room during your transvaginal scan.
Transvaginal ultrasound is similar to a gynecological examination. You will be covered with sheet. A small ultrasound probe will be inserted into the vagina. The probe is moved in the vagina and picture taken.
Our Features
Features
Experienced Doctor
15 Yr. of Exp. & Well Trained Staff.
Advanced Machine
Equipped with cutting edge technology infrastructure helps to improve health of mother & baby .
Trained Staff
Well Trained Staff at Clinic
4.9 Rated on Google
1200+ Reveiws on Google & Counting.

Our Doctor
Dr Vinod Jogdand
( Fetal Medicine Consultant)
Trained in Fetal medicine in Kings college Hospital Denmark Hill, London, England under Professor Kypros Nicolaides. Trained in Obstretic Ultrasound from Mediscan, Chennai. Trained in Infertility from FOGSI recognised Hospital, Gujarat.